Laboratory of Biochemistry
Staff
Susumu Itoh, Ph.D.Professor
Etsu Tashiro, Ph.D.Associate Professor
Naoko Nakano, Ph.D.Senior Assistant Professor
Yoshimi Uchida, Ph.D.Assistant Professor
TGF-&beta Signaling and Its Implication in Tumor Development
TGF-&beta (transforming growth factor-&beta) is known to inhibit the cell proliferation in anumber of cells. Mutations in molecules indispensable for TGF-&beta signaling lead totumorigenicity. In addition, the abnormal acceleration of TGF-&beta signaling induces fibrosis invarious tissues and organs because TGF-&beta promotes the production of extracellular matrixproteins (ex, fibronection, collagen, PAI-1 etc.).
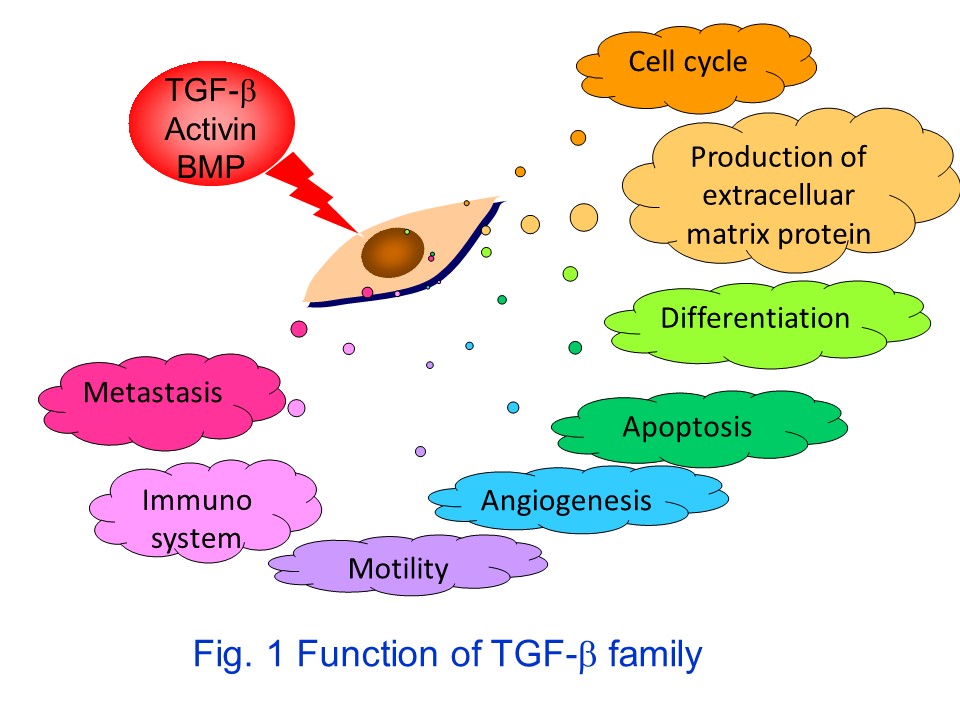
TGF-&beta family consists of 33 related cytokines including TGF-&beta s, activins and BMPs(bone morphogenetic proteins), which regulate apoptosis, cell differentiation, immunesurveillance, cell motility and angiogenesis and play key roles in embryogenesis and maintenanceof tissue homeostasis during adult life.
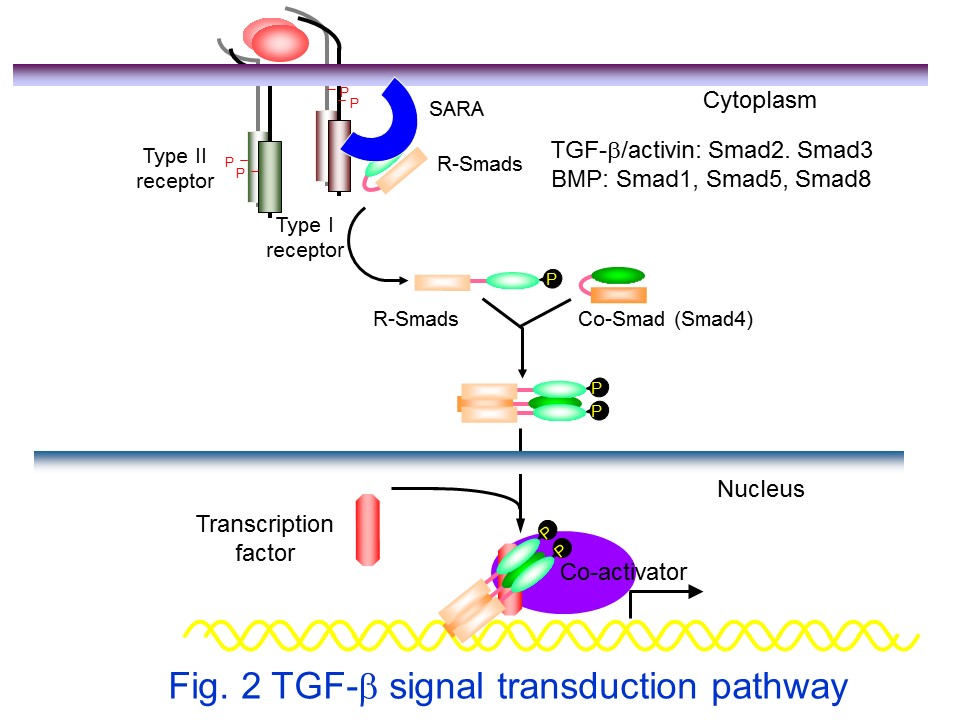
The TGF-&beta family signals via specific serine/threonine kinase receptors and intracellularsignal transducing molecules, termed Smads. TGF-&beta signaling is initiated by ligand binding toTGF-&beta type II receptor (T&betaRII), which induces the formation of heteromeric complexesbetween specific TGF-&beta type I receptor (T&betaRI) and T&betaRII serine/threonine kinases.T&betaRI [also termed activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)5] is phosphorylated and activated byT&betaRII. Active T&betaRI catalyzes the C-terminal serine phosphorylation of receptor-regulated (R-)Smads, Smad2 and Smad3 which are presented to active ALK5 kinase by an adaptorprotein, SARA (Smad anchor for receptor activation). After phosphorylation, R-Smads can form aternary complex with a common-partner Smad4 and then translocate to the nucleus, where theyregulate the transcription of TGF-&beta target genes.
We found that the TGF-&beta direct target gene TMEPAI (transmembrane prostate androgen-induced RNA), whose expression is often increased in several tumors, blocks TGF-&betasignaling. TMEPAI competes with SARA for R-Smad binding, thereby sequestering R-Smadsfrom T&betaRI kinase activation
When we searched for a family molecule(s) for TMEPAI, we found C18ORF1which also inhibitsTGF-&beta signal like TMEPAI although C18ORF1 expression is not affected by TGF-&beta.Thus, it is supposed that C18ORF1 and TMEPAI form TMEPAI family. Our present study is toelucidate how TMEPAI specifically perturbs TGF-&beta signaling in detail; (2) how TMEPAI isinvolved in tumorigenicity.
Except for TMEPAI study, we also investigate how BMP signal is involved in chondrocyte andadipocyte differentiation. Furthermore, we explore seeds for anti-cancer drug(s) which inhibitsTGF-&beta signal.