Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry of Medicines
Staff
Satoru Karasawa, Ph.D.Professor
Kazuteru Usui, Ph.D.Associate Professor
Noriko Suzuki, Dr. Sci.Senior Assistant Professor
Shota Matsumoto, Ph.D.Assistant Professor
Brief Overviews of our Research
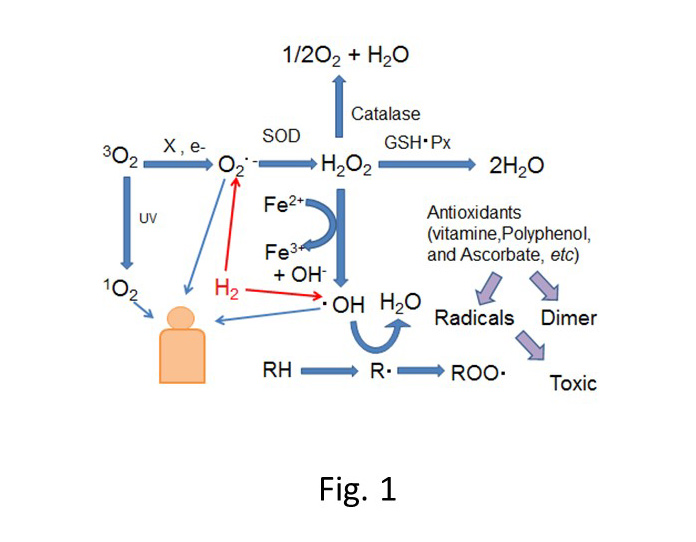
(a) Design of potent antioxidants.
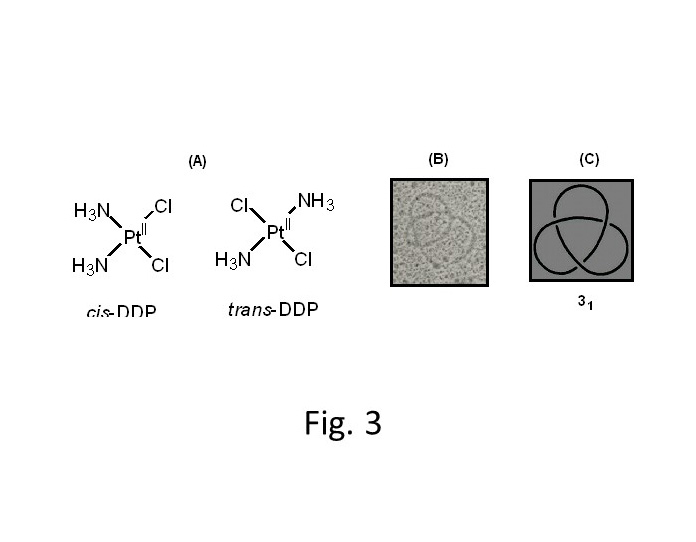
(b)TEM and structual studies of cisplatine-DNA topology.
(c)Approach to understand mechanism of Aβ 1-42 aggregation.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as the hydroxyl radical (HO . ), superoxide (O 2 -. ),and hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) have high oxidative strength, abstract electrons andhydrogen radicals from biological targets, and cause oxidative damage in vitro (Fig. 1).
Recently, we showed that the aggregation of Aβ 1-42 is different in several pH solutions,and TEM images (x 28000) of Aβ self-assembly are represented in Fig. 2.
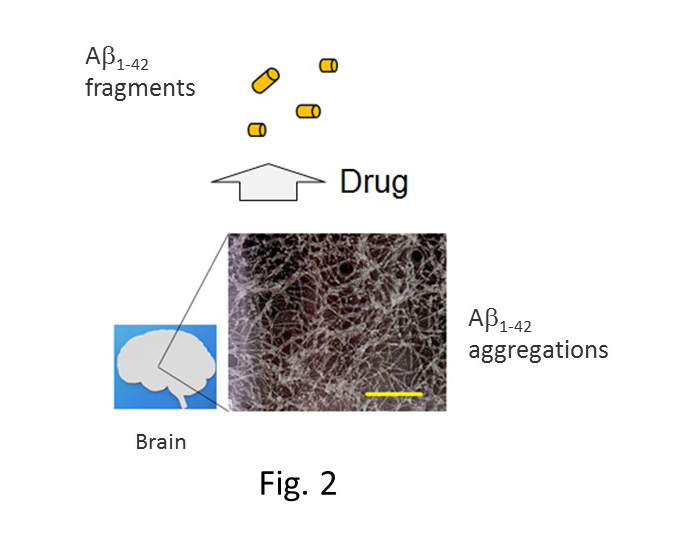
The aggregation model plays an important role in the design and synthesis of inhibitorsof Aβ aggregation.
cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum(II), Pt II (NH3)2 Cl2 (cisplatin or cis-DDP) is a most usefulanti-cancer agent in cancer chemotherapy (see Fig. 3(A)). However, the trans-isomer(trans-DDP) of cis-DDP is clinically ineffective although it binds to DNA. We are interestedin the difference of anti-cancer activity (geometrical effect) of the two drugs. Figures 3(B)and (C) show the TEM images of trefoil DNA which produced under the DNAtopoisomerase I-reaction condition in living nucleus model (cis-DDP modified DNA-histone complex) and the topology 31 . The topological production caused by binding ofanti-cancer drug, cisplatin, to DNA-histone complex. The results may be a measure forthe development of new anti-cancer drugs.complex.
Basic study and Application of clay minerals.
The environmental purification and conservation by some clay minerals have beenresearched. Smectite group is mainly used on our study.